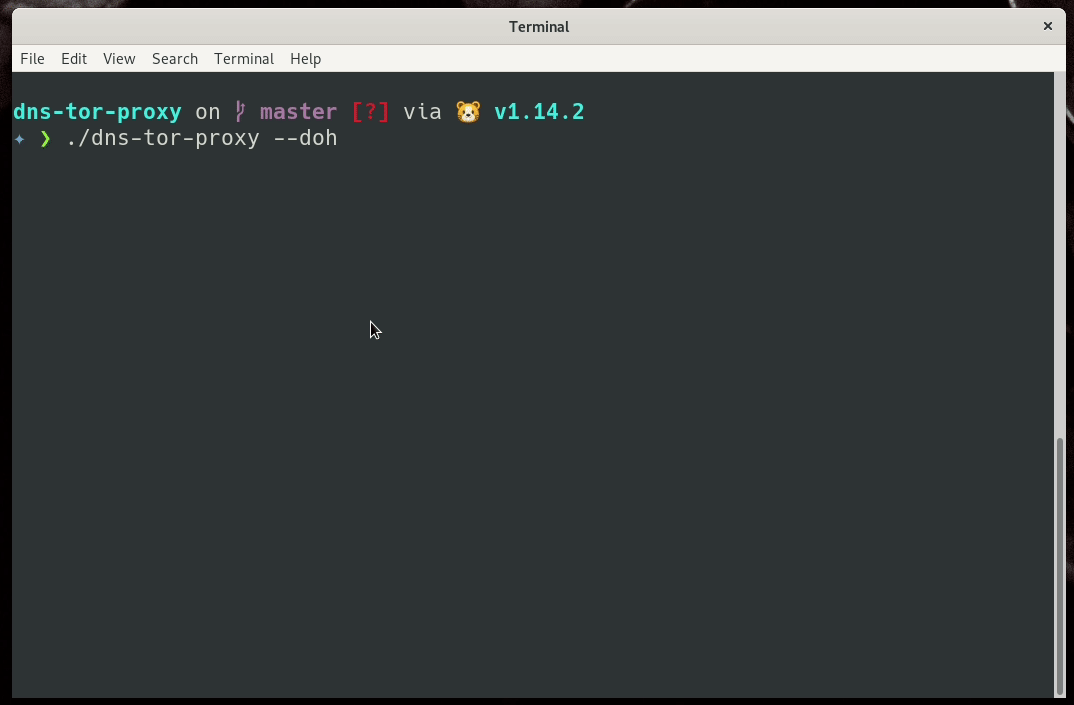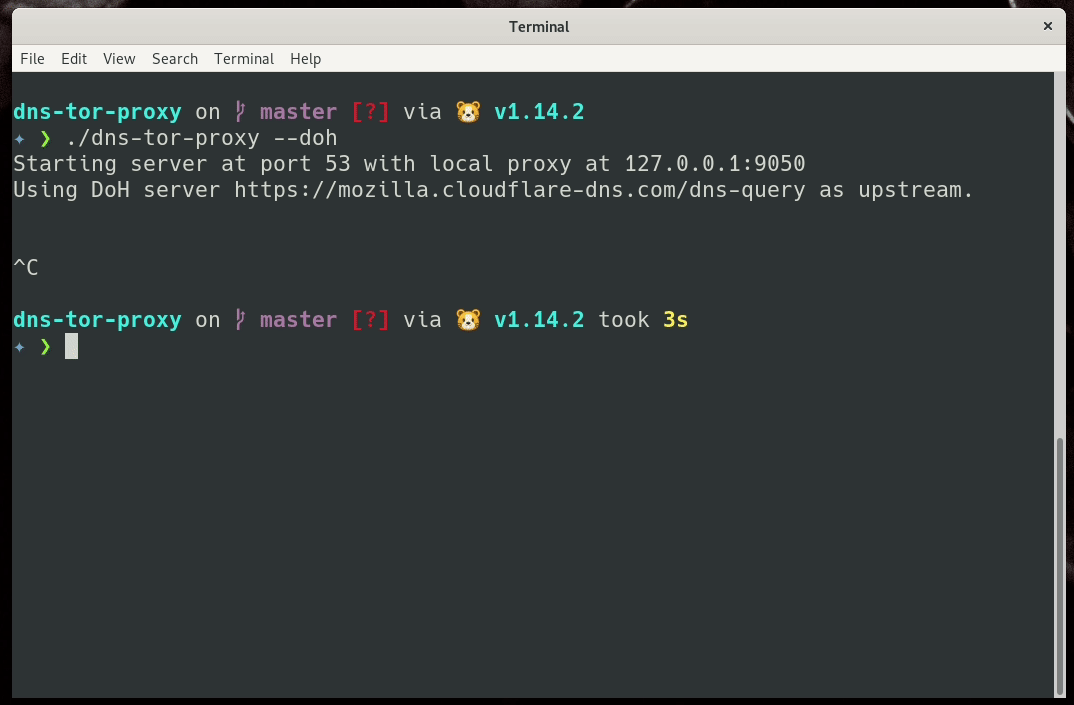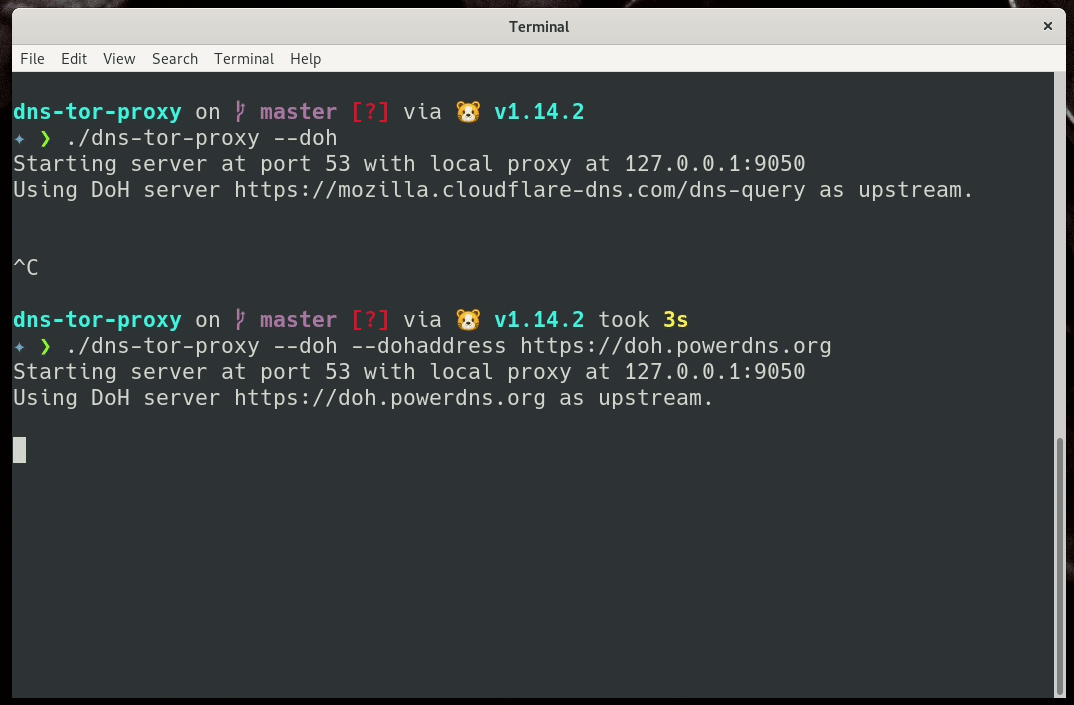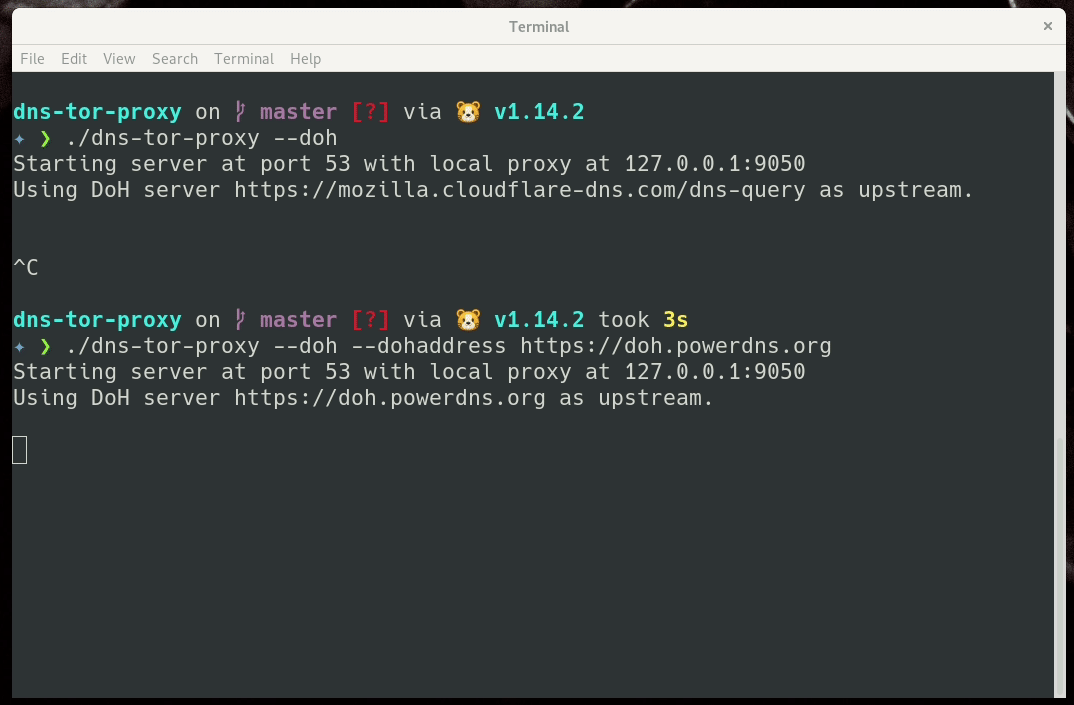
Use DoH over Tor for your Qubes system
I was using my dns-tor-proxy tool in the AppVMs in my QubesOS system. But, at the same time I was trying to figure out how to make it the default DNS system for the whole Qubes.
ahf provided me a shell script showing how he is forwarding the DNS requests to a VPN interface. I modified the same so that all of standard DNS queries become DoH queries over the Tor network.
Setting up sys-firewall
In the following example, I am setting up the sys-firewall service VM. All
other AppVMs connected to this VM as netvm will be use dns-tor-proxy without
any modification.
Make sure that the template for sys-firewall has the latest Tor installed. You
can get it from the official Tor
repository.
Download (or build) the latest dns-tor-proxy 0.3.0
release, and put the file
(as executable) in /rw/config/ directory.
Next, modify the /rw/config/rc.local file & add the following lines.
systemctl start tor
sh /rw/config/dns.sh
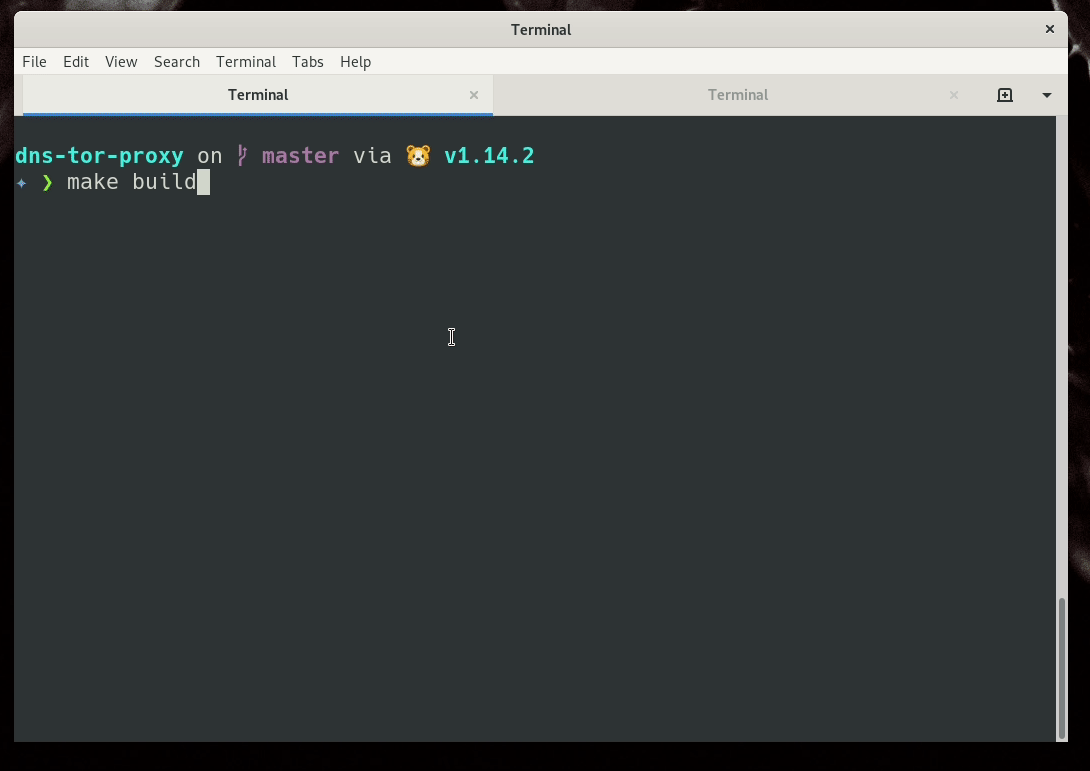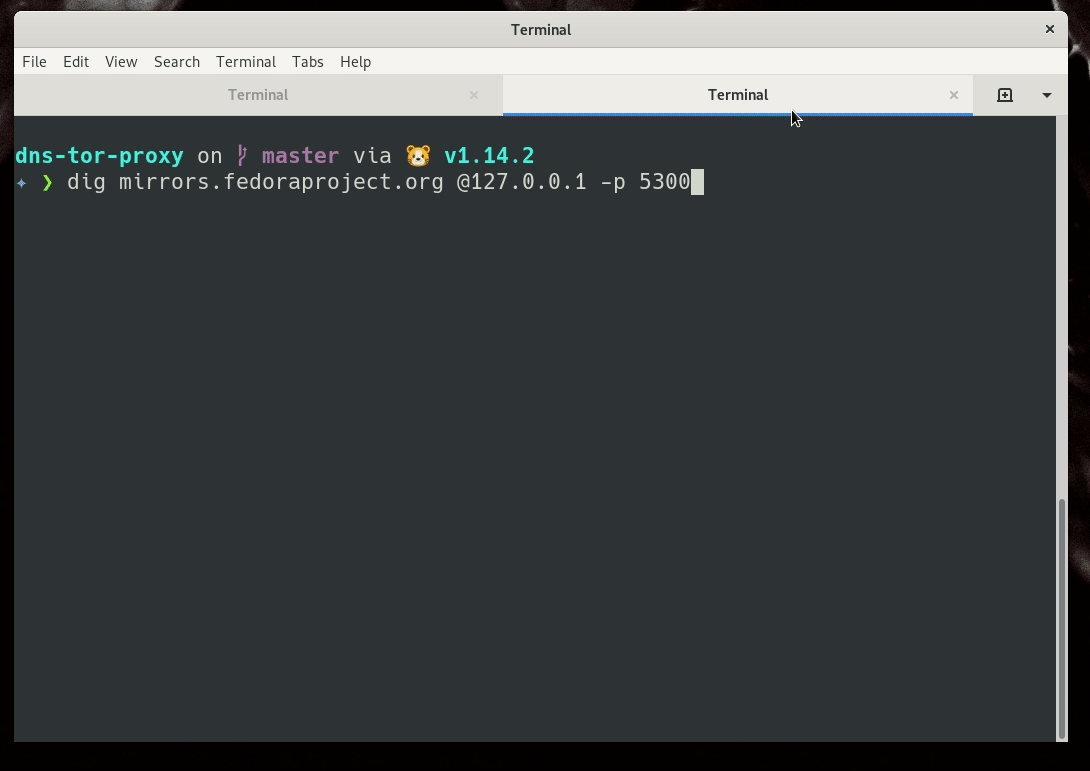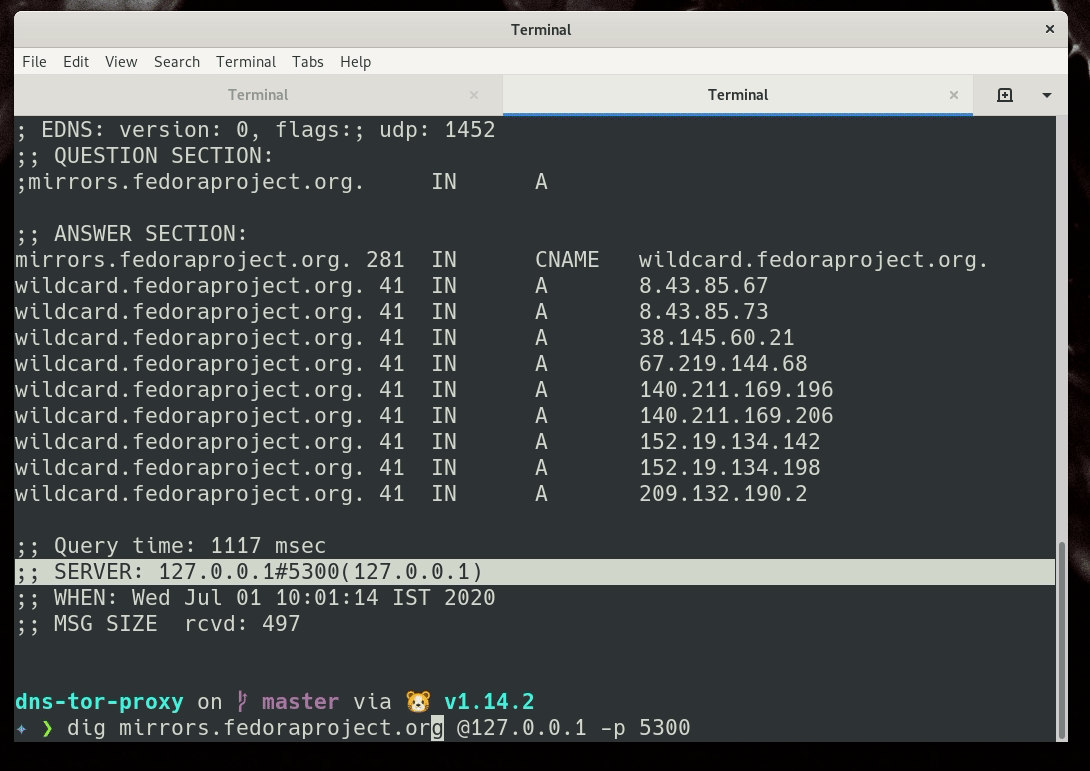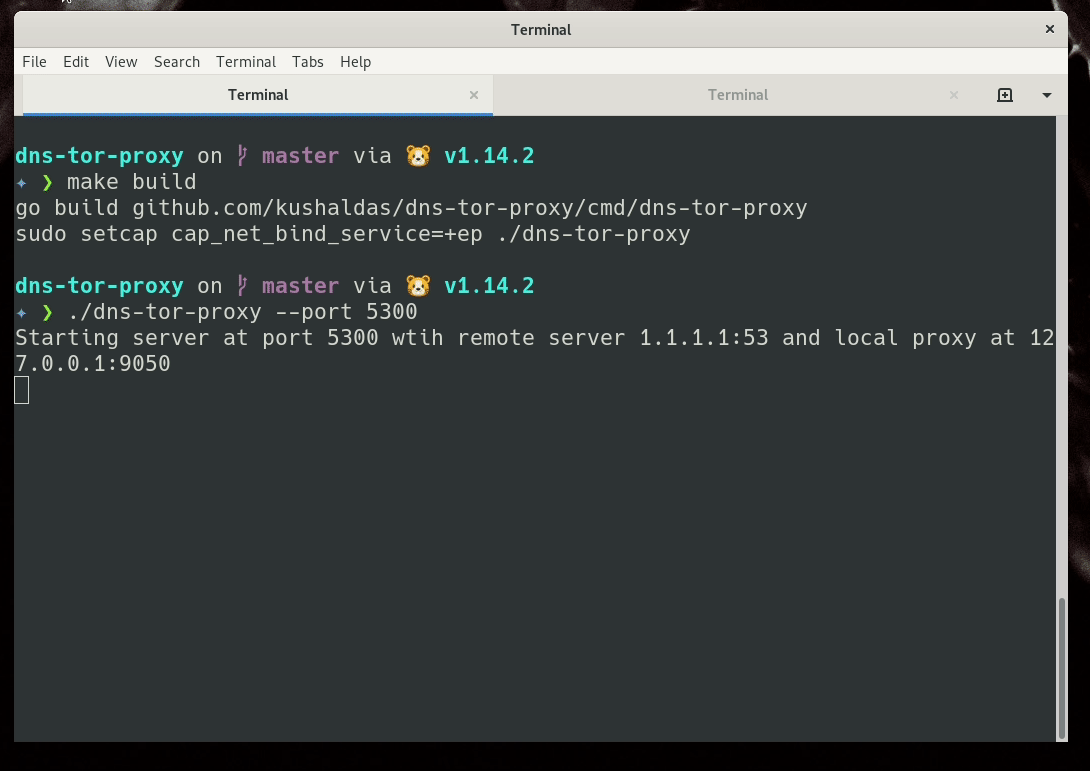
/rw/config/dns-tor-proxy --doh &
As you can see, we are executing another script at /rw/config/dns.sh, which
has the following content. Remember to modify the DNS value to the right IP for
your sys-firewall vm.
#!/bin/sh
QUBES_DNS_SERVERS="10.139.1.1 10.139.1.2"
DNS=10.137.0.x
# accept DNS requests from the other vms
iptables -I INPUT -i vif+ -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
iptables -I INPUT -i vif+ -p tcp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
# Clean up our NAT firewall rules.
iptables --flush PR-QBS --table nat
# We take incoming traffic on TCP and UDP port 53 and forward to
# our DNS server.
for QUBES_DNS_SERVER in ${QUBES_DNS_SERVERS} ; do
iptables --append PR-QBS --table nat --in-interface vif+ --protocol tcp --destination "${QUBES_DNS_SERVER}" --dport 53 --jump DNAT --to-destination "${DNS}":53
iptables --append PR-QBS --table nat --in-interface vif+ --protocol udp --destination "${QUBES_DNS_SERVER}" --dport 53 --jump DNAT --to-destination "${DNS}":53
done
# Log *other* DNS service connections. This part is optional, but ensures that
# you can monitor if one of your VM's is making any traffic on port 53 with
# either TCP or UDP. If you want to log *every* DNS "connection", including the
# ones to QUBES_DNS_SERVERS, you can either move these commands up before the
# for-loop in this file or change the --apend option to be an --insert instead.
iptables --append PR-QBS --table nat --in-interface vif+ --protocol tcp --dport 53 --jump LOG --log-level 1 --log-prefix 'DNS Query: '
iptables --append PR-QBS --table nat --in-interface vif+ --protocol udp --dport 53 --jump LOG --log-level 1 --log-prefix 'DNS Query: '
Now, restart your sys-firewall vm. And you are all set for your DNS queries.